Builders
The extended_builder option enables you to extend the creation process with user extensible creation. It is intended to accommodate cases where DBMSs provide proprietary features - such as Table Valued Functions (TVFs) - that should be exposed as APIs.
Overview
Here is a general overview of creating projects using an extended builder.
1. Create your_builder.py
This is a Python file that creates <project_directory>/api/your_api_extension.py, with:
def extended_builder(db_url, project_directory):
""" called by ApiLogicServer CLI -- scan db_url schema, create your_api_extension.py
for each database object:
class t_<db-object-name> -- the model
class <db-object-name> -- the service
args
db_url - use this to open the target database, e.g. for meta data
project_directory - the created project... create / alter files here
"""
2. Create Project
Specify the --extended_builder=your_builder.py option. The system will invoke your builder, which operates as described below.
2a. Database Introspection
Use the db_url to open your database, and find database objects you wish to expose
2b. Project File Creation
Create <project_directory>/api/your_api_extension.py. This executes your api extensions. It generally contains
- SQLAlchemy class definitions for results, e.g.
t_udfEmployeeInLocation = Table( # define result for udfEmployeeInLocation
"udfEmployeeInLocation", metadata,
Column("Id", Integer),
Column("Location", String(50)),
Column("Name", String(50)))
- API Implementations, e.g.
class udfEmployeeInLocation(JABase):
"""
description: define service for udfEmployeeInLocation
"""
_s_type = "udfEmployeeInLocation"
@staticmethod
@jsonapi_rpc(http_methods=['POST'], valid_jsonapi=False)
def udfEmployeeInLocation(location):
"""
description: expose TVF - udfEmployeeInLocation
args:
location : value
"""
2c. Runtime activation
Ensure your_api_extension.py is activated at server startup time, e.g. by updating <project_directory>/api/customize_api.py
Example - TVF
Install as usual, and create your project using the extended_builder option, e.g:
ApiLogicServer run --db_url='mssql+pyodbc://sa:Posey3861@localhost:1433/SampleDB?driver=ODBC+Driver+18+for+SQL+Server&trusted_connection=no&Encrypt=no' \
--extended_builder=extended_builder.py \
--project_name=TVF
Or, use the default extended_builder:
ApiLogicServer create --db_url='mssql+pyodbc://sa:Posey3861@localhost:1433/SampleDB?driver=ODBC+Driver+18+for+SQL+Server&trusted_connection=no&Encrypt=no' \
--extended_builder='*' \
--project_name=TVF
to designate a file that implements your builder. During the creation process, the system will invoke extended_builder(db_url, project_directory) so you can add / alter files as required. In this example, the output file <project_directory>/api/your_api_extension.py is named <project_directory>/api/tvf.py
Full automation for specific DBMS features was considered, but could not conceivably accommodate all the DBMS features that might be desired. We therefore provide this extensible automation approach.
Let's illustrate the use of extensible automation with this example. Create the sample project as follows:
- Acquire this sql/server docker database
- Create the project
docker run -it --name api_logic_server --rm -p 5656:5656 -p 5002:5002 -v ${PWD}:/localhost apilogicserver/api_logic_server
ApiLogicServer create --project_name=/localhost/sqlserver-types --extended_builder='*' --db_url=mssql+pyodbc://sa:Posey3861@localhost:1433/SampleDB?driver=ODBC+Driver+17+for+SQL+Server?trusted_connection=no
This uses an example extended builder can be found here. You can copy this file to a local directory, alter it as required, and specify its location in the CLI argument above. It is loosely based on this example.
The interface to ApiLogicServer requires that you provide an extended_builder(db_url, project_directory) function, like this (the rest is up to you):
def extended_builder(db_url, project_directory):
""" called by ApiLogicServer CLI -- scan db_url schema for TVFs, create api/tvf.py
for each TVF:
class t_<TVF_Name> -- the model
class <TVF_Name> -- the service
args
db_url - use this to open the target database, e.g. for meta data
project_directory - the created project... create / alter files here
"""
print(f'extended_builder.extended_builder("{db_url}", "{project_directory}"')
tvf_builder = TvfBuilder(db_url, project_directory)
tvf_builder.run()
This particular example creates this tvf file in the api folder.
Updates api/customize_api.py to expose it, as shown below:
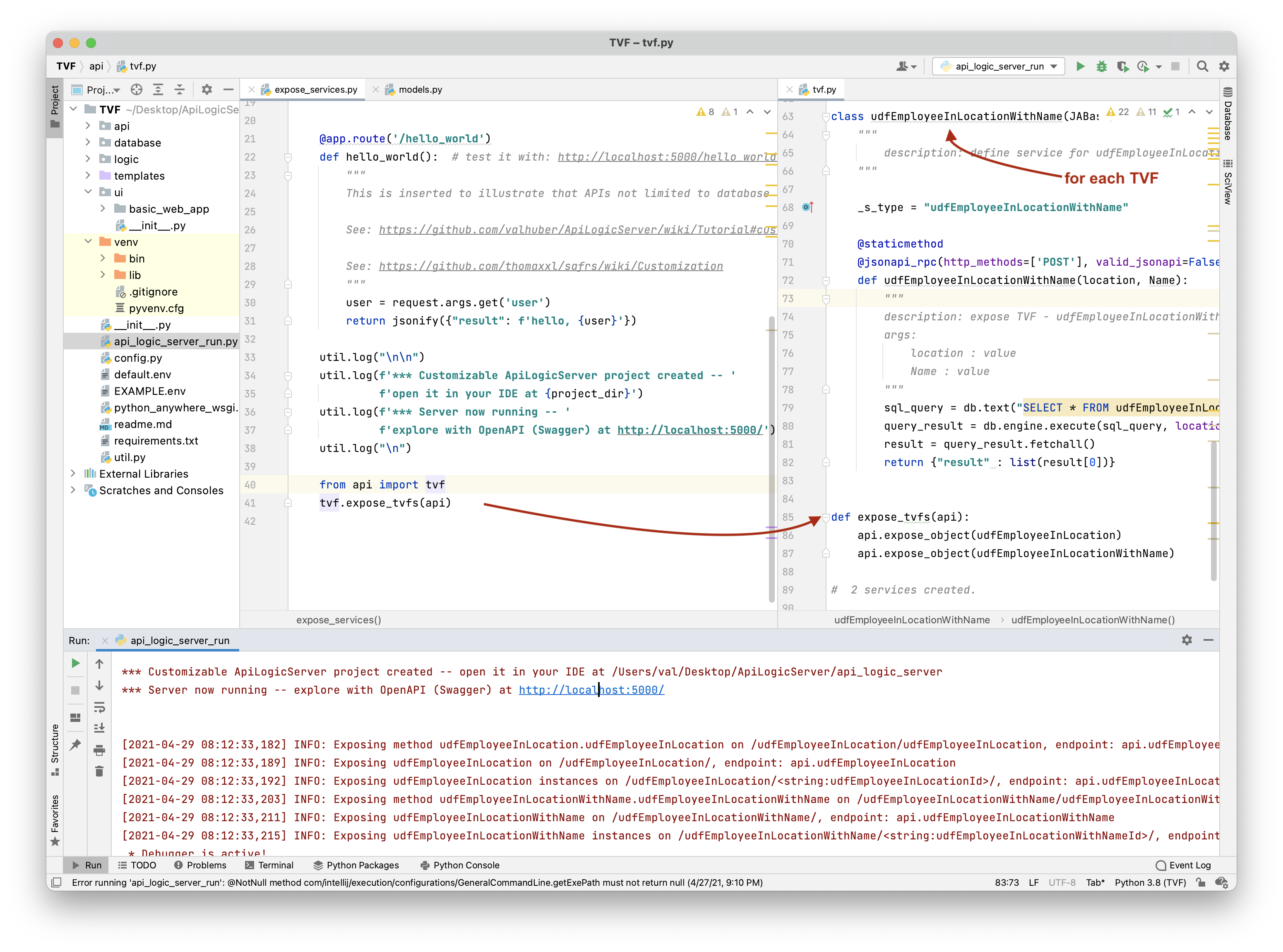
This example illustrates the extended builder approach; the resultant services runs as shown below.
It does not deal with many data types.
It generates Swagger, with arguments:
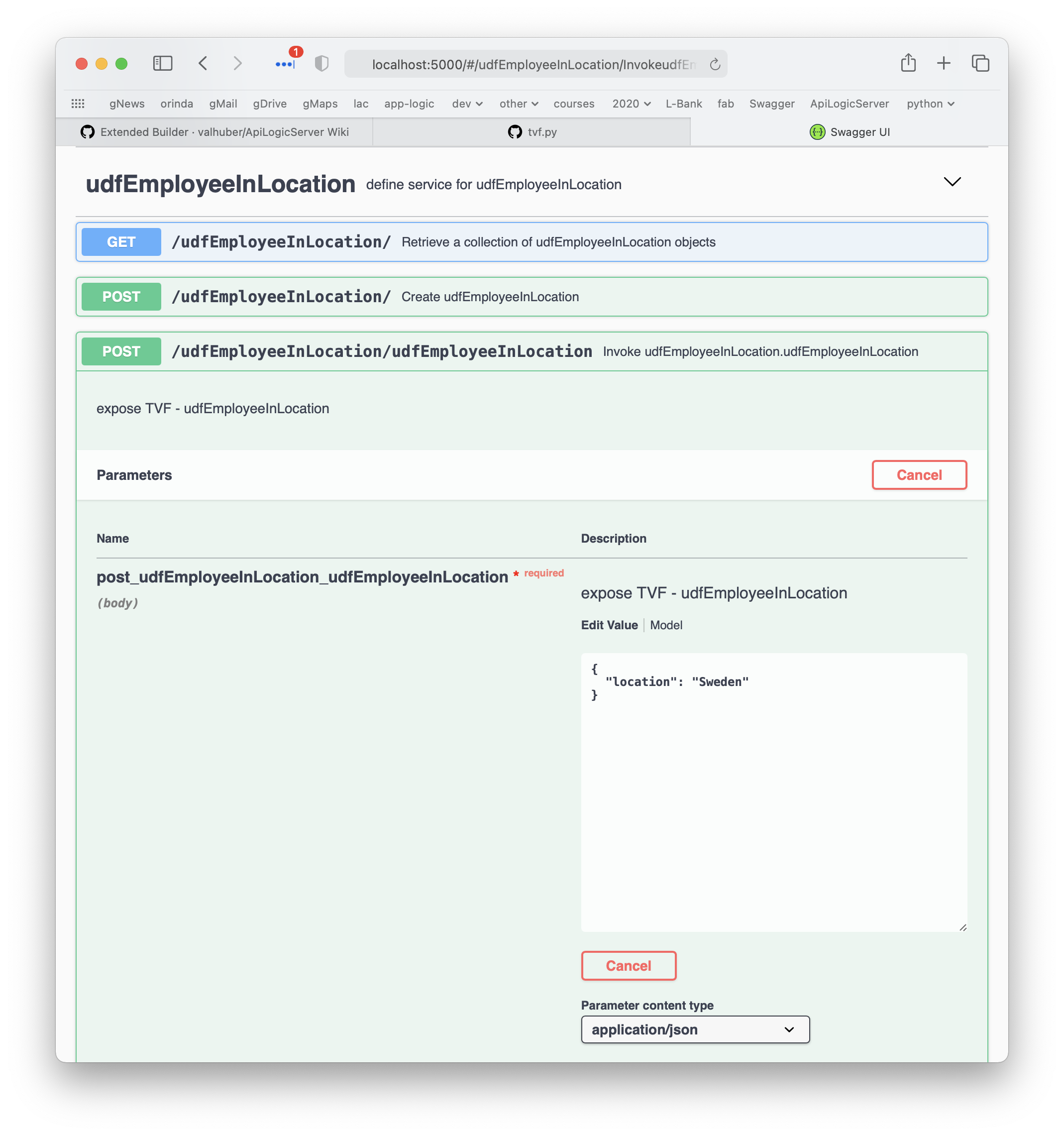
You can run it with this cURL:
curl -X POST "http://localhost:5656/udfEmployeeInLocation/api/udfEmployeeInLocation" -H "accept: application/vnd.api+json" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d "{ \"location\": \"Sweden\"}"
returns the expected data: