Managed Database

This page explains how to:
-
create a resource group
-
create a managed database
-
deploy an API Logic Project image from DockerHub
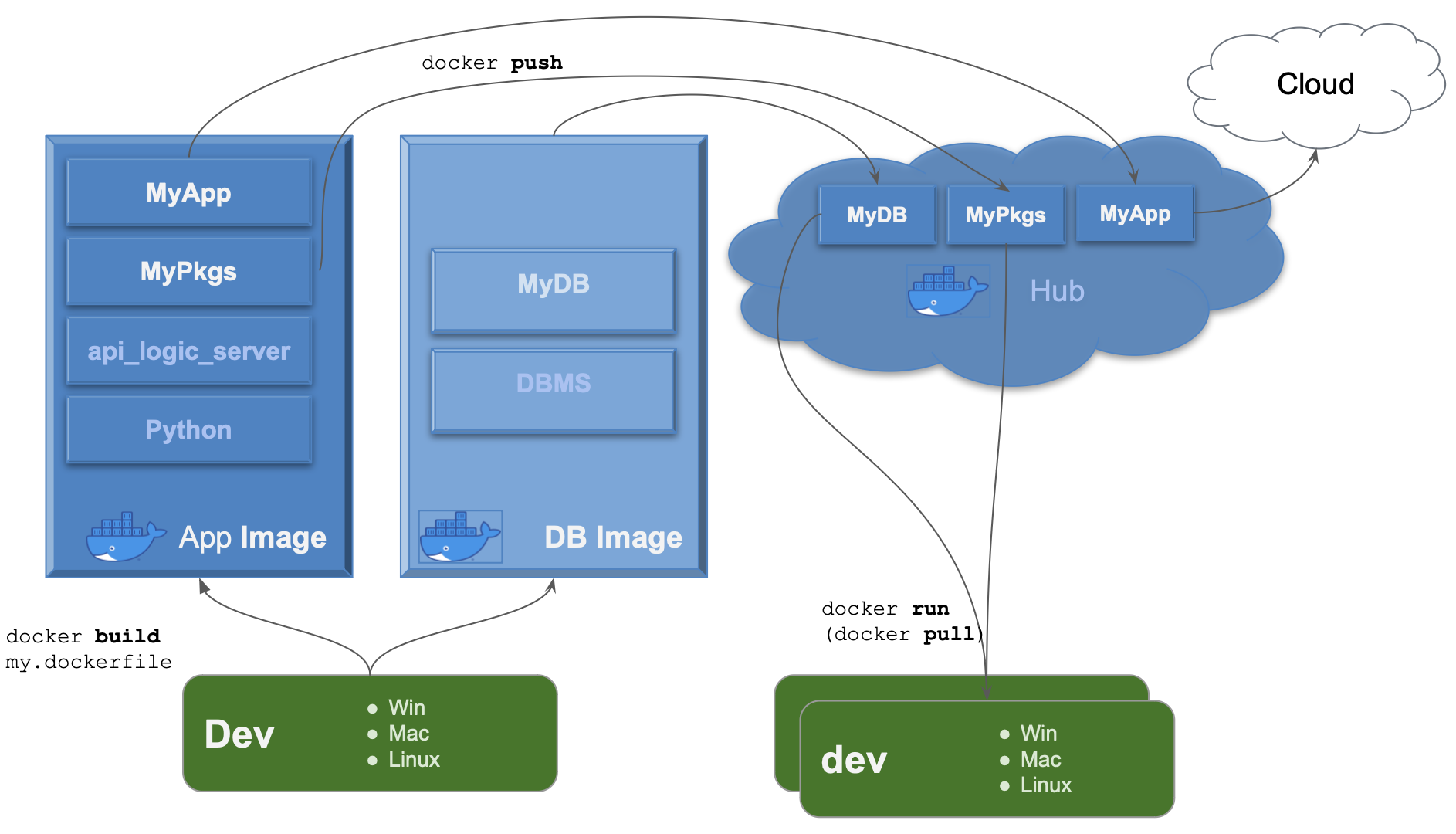
Containers are a best practice for deployment, and offer several advantages for development. This outlines a typical scenario for deploying API Logic Server projects to Azure.
This tutorial presumes you've already pushed an image, here called apilogicserver/docker_api_logic_project:latest.
Create Azure Account
I created a free account, electing the $200 free option. In the entire exercise, I used less than $2 of my allotment.
Create Managed Database
Creating the database was straightforward using Microsoft documentation. To see it, click here.
Note: we used the database name
nwlogic.
Note this is a managed database, which means that Azure will apply DBMS updates, take backups, etc. Contrast this to running a database in a bare container, where you'd need to arrange such services yourself.
Container Group
The database creation wizard requires that you create a container group.
database nwlogic
For this tutorial we created the database nwlogic. It is an exact replica of the sample (nw) sample database), using SqlServer.
Load Data: Azure Data Tools
After creating the database, load the data using tools like PyCharm Data Tools, or DbVis.
To find the sql scripts, click here.
Portal
Create Container
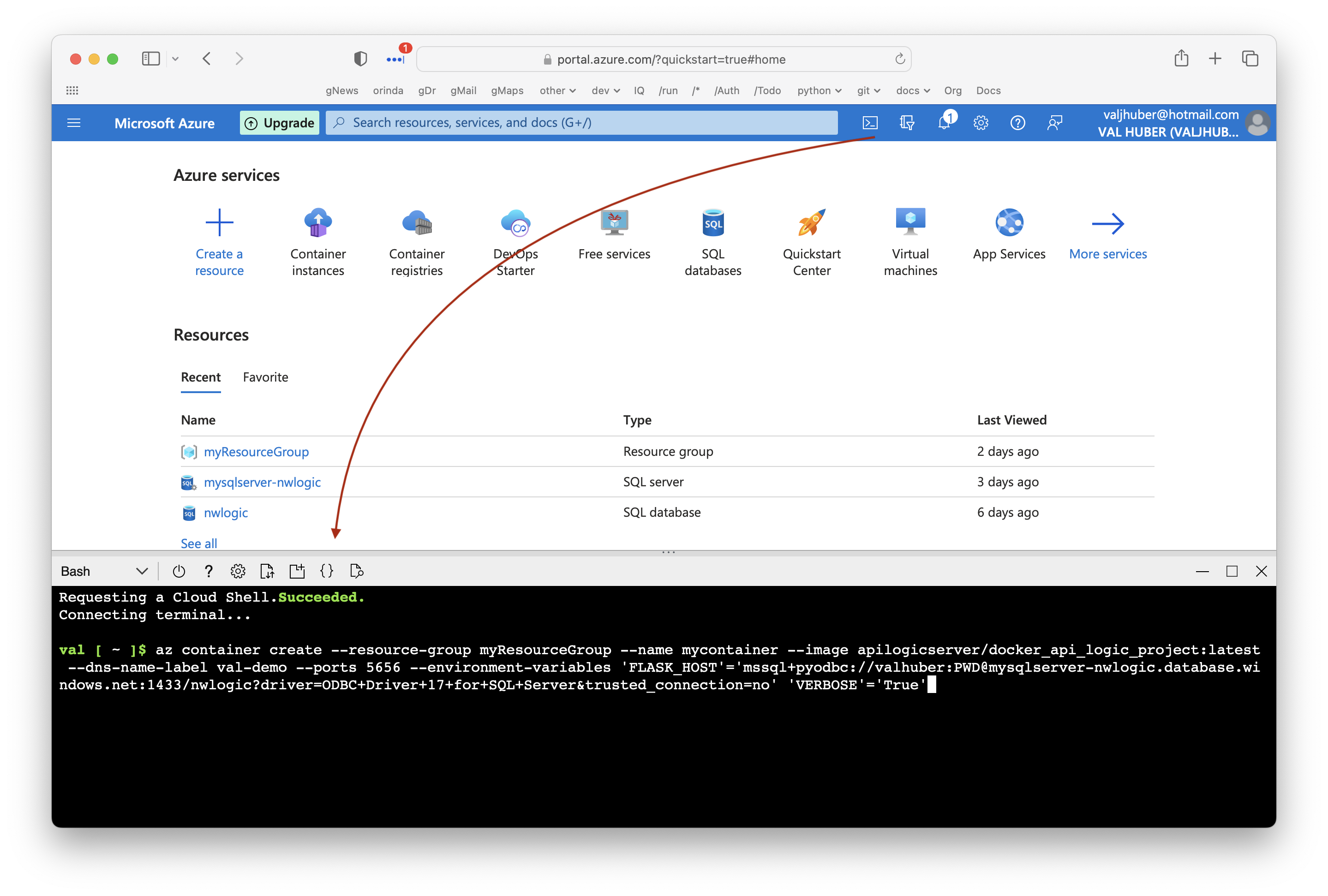
az container create --resource-group myResourceGroup --name mycontainer --image apilogicserver/docker_api_logic_project:latest --dns-name-label val-demo --ports 5656 --environment-variables 'FLASK_HOST'='mssql+pyodbc://valhuber:PWD@mysqlserver-nwlogic.database.windows.net:1433/nwlogic?driver=ODBC+Driver+17+for+SQL+Server&trusted_connection=no' 'VERBOSE'='True'
Most of the arguments are straight-forward, identifying the Docker Hub repository (apilogicserver/docker_api_logic_project:latest), the container group.
Note the
--environment-variablesare used to communicate the database and server location:--environment-variables 'FLASK_HOST'='mssql+pyodbc://valhuber:PWD@mysqlserver-nwlogic.database.windows.net:1433/nwlogic?driver=ODBC+Driver+17+for+SQL+Server&trusted_connection=no' 'VERBOSE'='True'
Recreate the container
If you need to recreate the container, you can use the portal, or this command:
Run Admin App
The create command above starts the server. After that, you can run the admin app: http://val-demo.eastus.azurecontainer.io:5656/.
Trouble Shooting
Use this command to view Azure logs:
For specific error conditions, see Troubleshooting Azure.